Compounds Developed
|
|
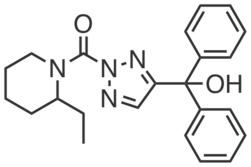
| Name: | ML226 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | 71304779 |
| CAS #: | 2055172-43-3 |
| Sys. name: | (2-ethylpiperidin-1-yl)(4-(hydroxydiphenylmethyl)-2H-1,2,3-triazol-2-yl)methanone |
| Mol. wt.: | 390.49 |
| Suppliers: | AOBIOUS Glixx Labs |
|
ML226 is a potent inhibitor of ABHD11, with an IC50 of 15 nM and least 100-fold selectivity for ABHD11 over all other serine hydrolases in soluble proteome derived from mouse T cells (~20), as assessed by gel-based competitive ABPP with fluorophosphonate-rhodamine. ML226 is also active in cells, where it completely and selectively inhibits ABHD11 at sub-nanomolar concentrations.
|
|
|
|
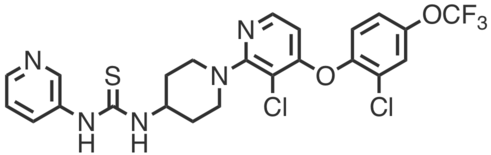
| Name: | DO264 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | 134813646 |
| CAS #: | 2301866-59-9 |
| Sys. name: | 1-(1-(3-chloro-4-(2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy)pyridin-2-yl)piperidin-4-yl)-3-(pyridin-3-yl)thiourea |
| Mol. wt.: | 558.40 |
| Suppliers: | MedChemExpress DC Chemicals ProbeChem Glixx Labs |
|
DO264 is a potent, selective, in vivo active inhibitor of ABHD12 that was developed from a high-throughput screening lead. ABHD12 is an α/β hydrolase that cleaves lyso-phosphatidylserine (lyso-PS) lipids, which are signaling molecules that modulate immune function in vivo. DO264 potently inhibited ABHD12 in mouse brain membrane proteomes (IC50 value = 6.4 nM) as determined by gel ABPP experiments against FP-Rh (1 µM, 45 min, 37 °C). DO264 also inhibited lyso-PS hydrolytic activity in lysates from mouse brain membrane (IC50 value = 2.8 nM) and human THP-1 cells (IC50 value = 6.4 nM). DO264 (0.001–1 µM, 4 h) dose-dependently increased lyso-PS and 20:4 PS levels in THP-1 cells (2 - 5x), and in primary human macrophages (1.3 - 2x increase, 1 µM, 24 h). C57BL/6 mice treated with DO264 (i.p. / p.o.) showed dose-dependent elevations in brain lyso-PS lipids, with 30 mg·kg-1 being sufficient to produce the largest increases observed (2 - 5x). DO264 treated mice (30 mg·kg-1 i.p. daily) displayed heightened immune responses in the LCMV clone 13 (Cl13) model of immune challenge: treated animals had decreased overall survival rates (~-40% after 20 days) and lung fluid (bronchoalveolar lavage) from these mice showed increased total protein (~10x) and pro-inflammatory cytokines (~2-3x) relative to control-treated animals. Together, DO264, its inactive control analog (S)-DO271, and ABHD12–/– mice are powerful tools for understanding the biological function of ABHD12 and its pharmacological potential.
|
|
|
|
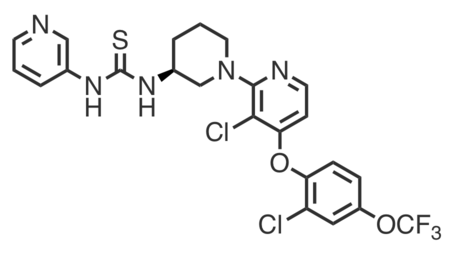
| Name: | (S)-DO271 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Control compound for DO264 |
| PubChem CID: | 134813650 |
| CAS #: | 2301865-01-8 |
| Sys. name: | 1-[(3S)-1-[3-chloro-4-[2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy]pyridin-2-yl]piperidin-3-yl]-3-pyridin-3-ylthiourea |
| Mol. wt.: | 558.40 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
(S)-DO271 is a structurally-similar, ABHD12-inactive analog of DO264 developed to control for potential off-target effects, particularly those that might occur due to the thiourea motif.
|
|
|
|
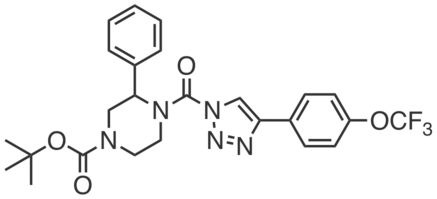
| Name: | DO53 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | 129188755 |
| CAS #: | 1848233-59-9 |
| Sys. name: | tert-butyl 3-phenyl-4-(4-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-1-carbonyl)piperazine-1-carboxylate |
| Mol. wt.: | 517.51 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
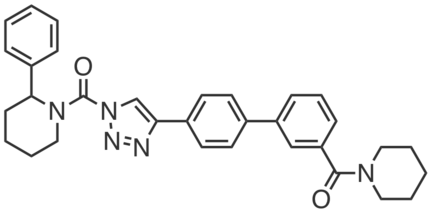
DO53 is a potent, in vivo active, covalent inhibitor of ABHD6, developed to control for the off-targets of DAGL inhibitors (including ABHD6) in vivo. DO53 selectively inhibited brain ABHD6 in mice (~100% inhibition at 10 mg·kg-1; >90% at 10 mg·kg-1; 4 h, i.p.) with almost no discernable off-targets by gel profiling (except PLA2G7 at 10 mg·kg-1). At higher doses, DO53 showed cross-reactivity with other serine hydrolases, including (>50% inhibition) PAFAH2, ABHD3, ABHD2, CES1C, and PLA2G7.
|
|
|
|
| Name: | KT185 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | 53364498 |
| CAS #: | 1472640-86-0 |
| Sys. name: | (2-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)(4-(3'-(piperidine-1-carbonyl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)methanone |
| Mol. wt.: | 519.65 |
| Suppliers: | Sigma |
|
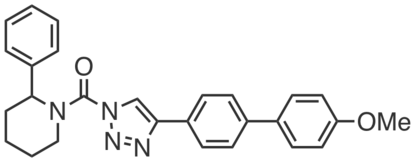
KT185 is a second-generation covalent inhibitor of ABHD6—developed specifically for this purpose—that shows increased potency and selectivity over previous inhibitors. KT185 is orally bioavailable, inhibiting ABHD6 in mouse brain (~100% inhibition at 40 mg·kg-1, i.p., 4 h; >70% at 20 mg·kg-1) with minimal cross-reactivity (other than CES1). Liver ABHD6 was completely inhibited at lower doses (~5–10 mg·kg-1). KT185 inhibited ABHD6 in the membrane fraction of mouse brain homogenates (100% inhibition at 10 nM, IC50 ~ 1 nM) with no observable serine hydrolase off-targets (up to 1 µM) and in Neuro2a cells (IC50 ~ 0.25 nM).
|
|
|
|
| Name: | KT195 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | 53364533 |
| CAS #: | 1402612-58-1 |
| Sys. name: | (4-(4'-methoxy-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)(2-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methanone |
| Mol. wt.: | 438.53 |
| Suppliers: | Sigma Cayman |
|
KT195 is a potent covalent inhibitor of ABHD6, initially developed alongside DAGLβ inhibitors to control for their off-targets. KT195 (IC50 = 10 nM) blocked fluorophosphonate-rhodamine labeling of ABHD6 in the membrane fraction of mouse brain homogenates and showed no appreciable cross-reativity with DAGLβ (10 µM). KT195 inhibited ABHD6 in Neuro2a cells (IC50 ~ 1 nM; ~100% at 10 nM) and showed negligible activity against other serine hydrolases (25 nM). Consistent with the notion that ABHD6 acts as a 2-AG hydrolase, KT195 (25 nM, 4 h) caused an elevation of cellular 2-AG levels in Neuro2A cells but had no effect on diacylglycerols or arachidonic acid. In mice, KT195 (5 mg·kg-1, i.p., 4 h) completely inhibited ABHD6 in peritoneal macrophages with minimal cross-reactivity (CES3, CES2G, and PLA2G15). |
|
|
|
| Name: | WWL70 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | 17759121 |
| CAS #: | 947669-91-2 |
| Sys. name: | 4'-carbamoyl-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl methyl(3-(pyridin-4-yl)benzyl)carbamate |
| Mol. wt.: | 437.50 |
| Suppliers: | Sigma Cayman TRC SCBT Ark Pharm Aurora |
|
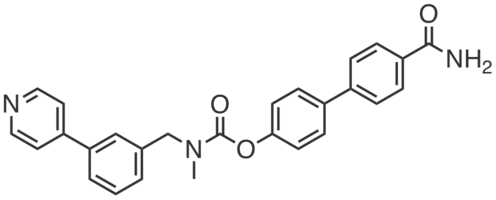
WWL70 is a first-generation potent and highly selective covalent inhibitor of the enzyme ABHD6, which hydrolyzes the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoyl glycerol. WWL70 blocked fluorophosphonate-rhodamine labeling of ABHD6 (IC50 = 70 nM) in membrane lysates from transfected HEK293T cells. Even at substantially higher concentrations (10 µM), WWL70 showed negligible cross-reactivity with other serine hydrolases in mouse brain membrane, with the exception of ABHD10 (~30% inhibition). Prentki et al. have also used WWL70 in DIO mice (10 mg·kg-1, i.p., daily for 8 weeks), which resulted in elevated markers of browning-related genes (e.g. Uncoupling protein 1) in visceral adipose tissue, akin to the effects observed in ABHD6 antisense oligonucleotide(ASO)-treated mice.
|
|
|
|
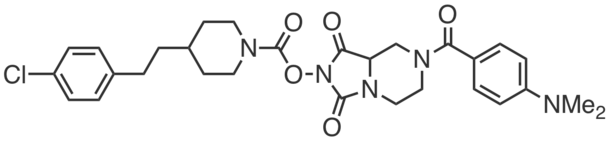
| Name: | ABC34 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Control compound for JJH260 |
| PubChem CID: | 118525588 |
| CAS #: | 1831135-56-8 |
| Sys. name: | 1,3-dioxo-7-(4-phenoxybenzyl)hexahydroimidazo[1,5-a]pyrazin-2(3H)-yl 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)piperazine-1-carboxylate |
| Mol. wt.: | 571.63 |
| Suppliers: | Cayman |
|
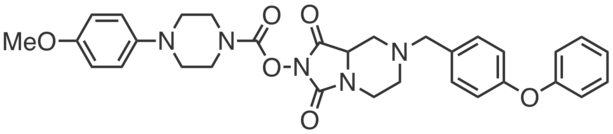
ABC34 is a control compound that is structurally similar to JJH260, most notably, containing the same reactive N-hydroxyhydantoin carbamate reactive group. Unlike JJH260, ABC34 (5 µM) did not react with AIG/ADTRP and can be used to control for the off-targets of JJH260 (e.g. ABHD6, PPT1, CES2). |
|
|
|
| Name: | JJH260 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | 71710928 |
| CAS #: | 1831135-30-8 |
| Sys. name: | 7-(4-(dimethylamino)benzoyl)-1,3-dioxohexahydroimidazo[1,5-a]pyrazin-2(3H)-yl 4-(4-chlorophenethyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate |
| Mol. wt.: | 567.22 |
| Suppliers: | Cayman |
|
JJH260 is a covalent inhibitor of AIG1 and ADTRP, two closely-related, atypical integral membrane hydrolases that can hydrolyze fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs). JJH260 blocked flurophosphonate rhodamine probe-labeling of AIG1 (IC50 = 0.5 µM) and ADTRP (IC50 = 8.5 µM) overexpressed individually in HEK293T cells. JJH260 had limited cross-reactivity with other serine hydrolases, which could be controlled for by using ABC34 (with the exception of LYPLA1/2). JJH260 also inhibited FAHFA hydrolysis by AIG1 in transfected HEK293T cells (IC50 = 0.6 µM) and at higher concentrations (5 µM), strongly inhibits (>80%) the FAHFA hydrolase activity in AIG1-transfected HEK293T cells, LNCaP cells, and membrane fractions from human T cells. |
|
|
|
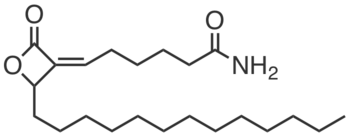
| Name: | KC01 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | 86289046 |
| CAS #: | 1646795-59-6 |
| Sys. name: | (Z)-6-(2-oxo-4-tridecyloxetan-3-ylidene)hexanamide |
| Mol. wt.: | 365.56 |
| Suppliers: | Cayman |
|
KC01 is a covalent inhibitor of AIG1 and ADTRP, two closely-related, atypical integral membrane hydrolases that can hydrolyze fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs). KC01 has a distinct reactive group (beta-lactone) from the N-hydroxyhydantoin carbamate JJH260. KC01 blocked fluorophosphonate-rhodamine labeling of AIG1 (IC50 = 0.2 µM) and ADTRP (IC50 = 1.3 µM) overexpressed individually in HEK293T cells. KC01 is less selective than JJH260 (cross-reacts with ABHD16A, PAFAH2, ABHD3, etc.), which can be largely controlled for by using ABC34. KC01 (5 µM), strongly inhibits (>80%) the FAHFA hydrolase activity in AIG1-transfected HEK293T cells, LNCaP cells, and membrane fractions from human T cells. |
|
|
|
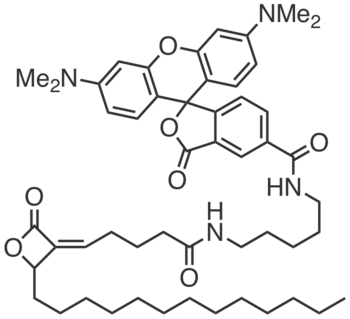
| Name: | WHP01 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Activity-based Probe |
| PubChem CID: | 86289026 |
| CAS #: | 1646795-61-0 |
| Sys. name: | (Z)-3',6'-bis(dimethylamino)-3-oxo-N-(5-(5-(2-oxo-4-tridecyloxetan-3-ylidene)pentanamido)pentyl)-3H-spiro[isobenzofuran-1,9'-xanthene]-5-carboxamide |
| Mol. wt.: | 849.13 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
WHP01 is a sensitive, fluorescent activity-based probe for AIG1 and ADTRP, which can be used to detect endogenous AIG1 and ADTRP activity in LNCap cells (2 µM, 30 min, 37 °C).
|
|
|
|
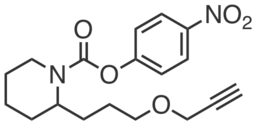
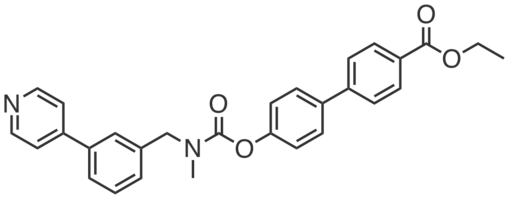
| Name: | JW972 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Activity-based probe |
| PubChem CID: | 72183486 |
| CAS #: | 1528560-41-9 |
| Sys. name: | 4-nitrophenyl 2-(3-(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)propyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate |
| Mol. wt.: | 346.38 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
JW972 is an alkyne-derivatized analog of WWL229 that can be used to selectively measure Ces3 activity. JW972 inhibits Ces3 recombinantly expressed in HEK293T cells (IC50 ~ 1.3 μM) but not Ces1f (IC50 > 20 μM).
|
|
|
|
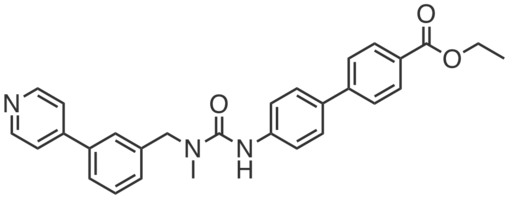
| Name: | WWL113 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | 17759482 |
| CAS #: | 947669-86-5 |
| Sys. name: | ethyl 4'-((methyl(3-(pyridin-4-yl)benzyl)carbamoyl)oxy)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate |
| Mol. wt.: | 466.54 |
| Suppliers: | Sigma Cayman Tocris TRC Aurum Pharamatech Aurora AkSci |
|
WWL113 is a potent, in vivo active, covalent inhibitor of mouse Ces3 (Ces1d) and Ces1f. It inhibits Ces3 and Ces1f recombinantly expressed in HEK293T cells (IC50 ~ 0.1 µM). It is also a potent inhibitor of human CES1 (IC50 = 46 nM), the homolog of mouse Ces3, in synthetic substrate hydrolysis assays. WWL113 promotes adipocyte differentiation and lipid storage in mouse 3T3-L1 and 10T1/2 preadipocytes. Treatment with WWL113 blocks basal lipolysis in mature adipocytes. In C57Bl/6 mice, a single 30 mg⋅kg−1 oral dose of WWL113 blocks >90% of liver and >75% of white adipose tissue Ces3 activity within 4 h. Chronic treatment of obese-diabetic db/db (30 mg⋅kg−1) or Diet Induced Obese (50 mg⋅kg−1) mice resulted in weight loss, normalization of plasma glucose and lipid profiles, improved glucose tolerance, increased insulin sensitivity, and a complete clearance of liver ectopic lipid deposits.”
|
|
|
|
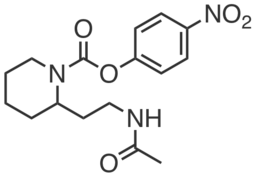
| Name: | WWL113U |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Control compound for WWL113 |
| PubChem CID: | 72183489 |
| CAS #: | 1528560-36-2 |
| Sys. name: | ethyl 4'-(3-methyl-3-(3-(pyridin-4-yl)benzyl)ureido)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate |
| Mol. wt.: | 465.21 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
WWL113U is a structurally related control compound for WWL113. Substitution of the carbamate group with a urea group renders WWL113U unable to inhibit Ces3 or Ces1f. WWL113U does not promote differentiation of preadipocytes or inhibit basal lipolysis in mature adipocytes. It also does not inhibit human CES1, the homolog of mouse Ces3.
|
|
|
|
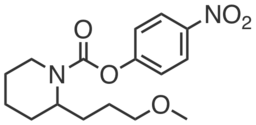
| Name: | WWL228 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Control compound for WWL229 |
| PubChem CID: | 72183488 |
| CAS #: | 1338575-27-1 |
| Sys. name: | 4-nitrophenyl 2-(2-acetamidoethyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate |
| Mol. wt.: | 322.15 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
WWL228 is a structurally related control compound for WWL229. It does not inhibit Ces3 or Ces1f recombinantly expressed in HEK293T cells (IC50 > 20 μM). WWL228 does not promote differentiation of preadipocytes or inhibit basal lipolysis in mature adipocytes.
|
|
|
|
| Name: | WWL229 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | 72183487 |
| CAS #: | 1338575-28-2 |
| Sys. name: | 4-nitrophenyl 2-(2-acetamidoethyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate |
| Mol. wt.: | 322.15 |
| Suppliers: | Sigma Cayman TRC Aurum Pharamatech AK Scientific |
|
WWL229 is a selective, covalent, carbamate inhibitor of Ces3 structurally distinct from WWL113. It inhibits Ces3 recombinantly expressed in HEK293T cells (IC50 = ~1.94 μM) but not Ces1f (IC50 > 20 μM). It shares with WWL113 the ability to promote differentiation of preadipocytes and inhibit basal lipolysis in mature adipocytes.
|
|
|
|
| Name: | HT01 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Activity-based probe |
| PubChem CID: | 60204011 |
| CAS #: | 1402658-23-4 |
| Sys. name: | N-(5-(3-(5,5-difluoro-7,9-dimethyl-5H-5l4,6l4-dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2',1'-f][1,3,2]diazaborinin-3-yl)propanamido)pentyl)-N-phenethyl-4-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-1-carboxamide |
| Mol. wt.: | 735.57 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
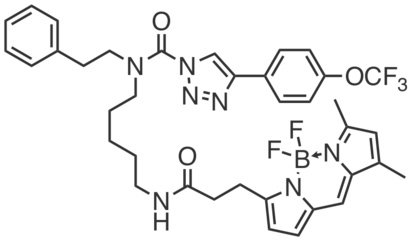
HT01 is a tailored activity-based probe that covalently reacts with DDHD2 and allows fluorescent gel profiling of native DDHD2 activity (e.g. 10 µM in Neuro2a membrane). HT01 also reacts with a small number of other serine hydrolases, including the diacylglycerol lipases DAGLα/β, some of which are challenging to detect with the more broad-spectrum fluorophosphonate probes.
|
|
|
|
| Name: | HT02 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Activity-based probe |
| PubChem CID: | 72712447 |
| CAS #: | 1402612-70-7 |
| Sys. name: | N-(5-(5-(2-oxohexahydro-1H-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl)pentanamido)pentyl)-N-phenethyl-4-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-1-carboxamide |
| Mol. wt.: | 687.78 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
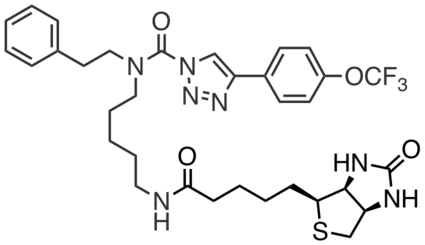
HT02 is a biotin analog of HT01, with similar target specificity, and can be used for the selective enrichment of DDHD2. |
|
|
|
| Name: | KLH40 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Control compound for KLH45 |
| PubChem CID: | 132274141 |
| CAS #: | - |
| Sys. name: | (R)-(3-benzylmorpholino)(4-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)methanone |
| Mol. wt.: | 432.40 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
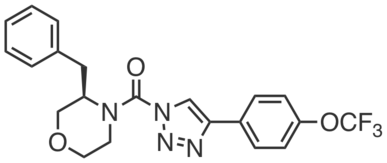
KLH40 is a control compound for KLH45 that reacts with ABHD6 with similar potency as the DDHD2 inhibitor KLH45 . KLH40 can be used to control for the ABHD6 off-target activity of KLH45, in cells (Neuro2a, IC50 ~ 10 nM) and in mice (20 mg⋅kg−1, i.p., every 12 h, 4 days). |
|
|
|
| Name: | KLH45 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | 126970670 |
| CAS #: | 1632236-44-2 |
| Sys. name: | N-cyclohexyl-N-phenethyl-4-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)-2H-1,2,3-triazole-2-carboxamide |
| Mol. wt.: | 458.49 |
| Suppliers: | Sigma Cayman Tocris R&D Systems |
|
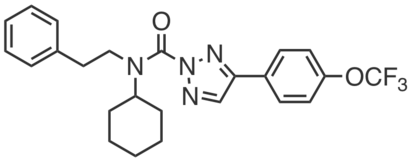
KLH45 is a potent triazole carbamate inhibitor (IC50 = 1.3 nM) of the brain triacylglyceride (TAG) hydrolase DDHD2. KLH45 is highly selective for DDHD2 over other serine hydrolases but does exhibit cross-reactivity with ABHD6, which can be controlled for by KLH40. KLH45 (20 and mg⋅kg−1, 4 h) resulted in near complete inhibition of DDHD2 in vivo. Whereas acute treatment (20 mg⋅kg−1, 4 h) did not result in altered brain TAGs, chronic dosing (20 mg⋅kg−1 every 12 h, 4 days) caused significant elevation (~1.5 fold) of TAGs in mouse brain. |
|
|
|
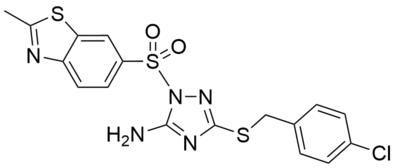
| Name: | PAL-12 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Activator |
| PubChem CID: | 405056735 |
| CAS #: | |
| Sys. name: | 3-((4-chlorobenzyl)thio)-1-((2-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-6-yl)sulfonyl)-5-amino-1H-1,2,4-triazole |
| Mol. wt.: | 452 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
PAL-12 is a direct, reversible activator of the catalytic activity of LYPLAL1. It stimulates a concentration-dependent 2.8- and 2.5-fold increase in FP-rhodamine labeling of purified mLYPLAL1 and hLYPLAL1, with an EC50 of 0.10 μM for mLYPLAL1. In synthetic substrate hydrolysis assays, PAL-12 increases the catalytic efficiency of purified mLYPLAL1, as reflected in compound-induced decreases in the Km value and increases in the Vmax value. Differential scanning fluorimetry thermal stability assays show that PAL-12 decreases the thermal stability of purified mLYPLAL1. In HepG2 cell lysates, PAL-12 increases LYPLAL1 activity 4-fold without affecting the activity of 55 other serine hydrolases, as assessed by MS-based ABPP-MudPIT experiments. Wild-type mice treated with PAL-12 show increased LYPLAL1 activity in liver (2-fold) and kidney (1.8-fold). Diet-induced obese mice treated with PAL-12 show improvements in glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity with no adverse effects noted.
|
|
|
|
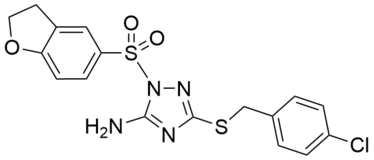
| Name: | PAL-4 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Activator |
| PubChem CID: | 405056727 |
| CAS #: | |
| Sys. name: | 3-((4-chlorobenzyl)thio)-1-((2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)sulfonyl)-5-amino-1H-1,2,4-triazole |
| Mol. wt.: | 422.9 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
PAL-4 is a direct, reversible activator of the catalytic activity of LYPLAL1. It stimulates a concentration-dependent 2.5- and 2.3-fold increase in FP-rhodamine labeling of purified mLYPLAL1 and hLYPLAL1, with half-maximal effective concentration (EC50) values of 0.39 and 0.49 μM, respectively. In synthetic substrate hydrolysis assays, PAL-4 increases the catalytic efficiency of purified mLYPLAL1, as reflected in compound-induced decreases in the Km value and increases in the Vmax value. for the enzyme. Shows selectivity over 49 other serine hydrolases quantified in MS-based ABPP-MudPIT experiments.
|
|
|
|
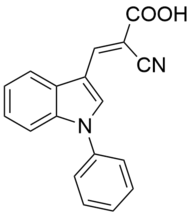
| Name: | UK-5099 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | |
| CAS #: | 56396-35-1 |
| Sys. name: | (E)-2-cyano-3-(1-phenyl-1H-indol-3-yl)acrylic acid |
| Mol. wt.: | 288.3060 |
| Suppliers: | Cayman Sigma MedChemExpress |
|
UK-5099 is an alpha-cyanocinnamate inhibitor of the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC) complex and was first discovered more than 30 years ago, though until recently, its precise mechanism of action and broader proteomic selecivity were poorly understood. Using the YY4-yne probe, we have provided evidence that UK-5099 shows excellent potency (IC50~ 0.02 μM) and proteomic selectivity for MPC2 in human cells. UK-5099 has been previously postulated to engage an (as of yet unidentified) cysteine on MPC1, but our data suggest instead that this compound may bind to C54 of MPC2 with a reversible covalent mechanism.
|
|
|
|
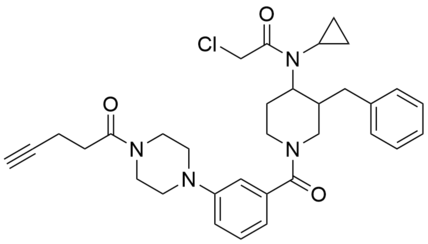
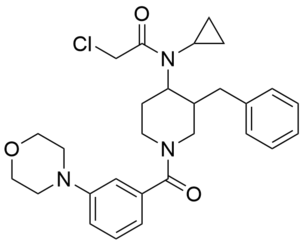
| Name: | YY4-yne |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Covalent probe |
| PubChem CID: | |
| CAS #: | |
| Sys. name: | N-(3-benzyl-1-(3-(4-(pent-4-ynoyl)piperazin-1-yl)benzoyl)piperidin-4-yl)-2-chloro-N-cyclopropylacetamide |
| Mol. wt.: | 575.1500 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
YY4-yne is a covalent probe based on YY4 and serves as a versatile cellular target engagement probe for MPC2 in click chemistry-enabled western blotting or global mass spectrometry-based proteomic experiments. Using YY4-yne, we demonstrated that UK-5099, an alpha-cyanocinnamate inhibitor of the MPC complex, first discovered more than 30 years ago, engages MPC2 with remarkable selectivity in human cells. These findings support a model where UK-5099 inhibits the MPC complex by binding to C54 of MPC2 in a covalent reversible manner that can be quantified in cells using the YY4-yne probe. |
|
|
|
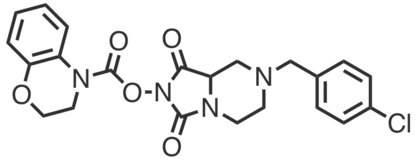
| Name: | YY4 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | |
| CAS #: | |
| Sys. name: | N-(3-benzyl-1-(3-morpholinobenzoyl)piperidin-4-yl)-2-chloro-N-cyclopropylacetamide |
| Mol. wt.: | 496.0480 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
YY4 is an alpha-chloroacetamide that covalently and irreversibly modifies cysteine-54 (C54) of the MPC2 subunit of the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC). YY4 has been shown to engage MPC2 in human T-cells with an IC50 of 0.88 μM (2h treatment). |
|
|
|
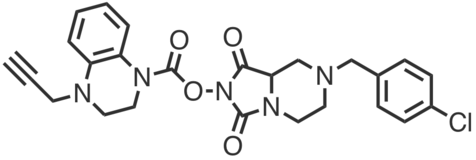
| Name: | ABC99 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | 134817170 |
| CAS #: | - |
| Sys. name: | 7-(4-chlorobenzyl)-1,3-dioxohexahydroimidazo[1,5-a]pyrazin-2(3H)-yl2,3-dihydro-4H-benzo[b][1,4]oxazine-4-carboxylate |
| Mol. wt.: | 456.88 |
| Suppliers: | Cayman AA Blocks DC Chemicals |
|
ABC99 is a potent and selective inhibitor of NOTUM, a secreted serine hydrolase that modulates Wnt signaling. Wnt proteins are post-translationally modified (palmitoleoylation, C18:1) on a conserved serine residue by the acyltransferase porcupine (PORCN) and deacylated by NOTUM. These events control Wnt pathway output which in turn affects biological processes such as tissue regeneration and cell proliferation. ABC99 strongly inhibited NOTUM in SW620 cell conditioned media (IC50 value = 13 nM, 2 h, 37 °C) as determined by competitive ABPP (FP-Rh) and showed no detectable activity across 64 additional serine hydrolases quantified by MS-ABPP in SW620 cells. ABC99 also preserved Wnt signaling (IC50 value = 89 nM) in a cell-based luciferase reporter assay of Wnt activation (HEK293T-STF cells), in which conditioned media (CM) from Wnt3A-producing L-cells was mixed with CM from NOTUM-producing SW620 cells. |
|
|
|
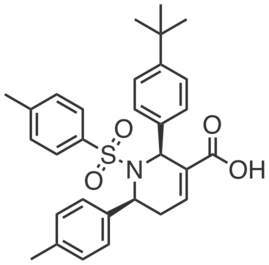
| Name: | ABC99yne |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Probe |
| PubChem CID: | |
| CAS #: | |
| Sys. name: | 7-(4-chlorobenzyl)-1,3-dioxohexahydroimidazo[1,5-a]pyrazin-2(3H)-yl 4-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroquinoxaline-1(2H)-carboxylate |
| Mol. wt.: | 493.95 |
| Suppliers: | |
|
ABC99yne is a sensitive, highly-selective “click”-able probe of NOTUM, based on ABC99. ABC99yne blocked NOTUM labeling by FP-Rh (IC50 value < 1 µM;, conditioned media from SW620 cells) and strongly labeled a single protein band at ~52 kDa, when “clicked” with rhodamine-azide; no other cross-reactive proteins were observed in conditioned media or cell lysates from SW620 cells (at 0.1 μM). |
|
|
|
| Name: | P11 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | 16656440 |
| CAS #: | 942285-55-4 |
| Sys. name: | cis-2-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)-6-(p-tolyl)-1-tosyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carboxylic acid |
| Mol. wt.: | 503.66 |
| Suppliers: | Cayman AK Scientific AOBIOUS Glixx Labs |
|
P11 is a non-covalent platelet activation factor acetylhydrolase (PAFAH) 1b2/1b3 inhibitor found through a fluorescence polarization-activity-based protein profiling screen of the National Institute of Health 300,000+ compound library. P11 inhibited PAFAH1b2 and PAFAH1b3 (IC50 values of ∼40 and 900 nM respectively) in a PAF substrate assay and showed no cross-reactivity with other brain serine hydrolases, including other PAFAHs such as PLA2G7 and PAFAH2. P11 (10 µM) also impaired the survival of PC3 and Neuro2a cancer cells by approximately 50%.
|
|
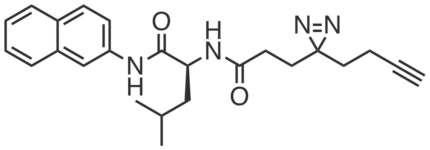
|
|
| Name: | CGP201725 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Photoaffinity probe / Gain-of-function ligand |
| PubChem CID: | 132274145 |
| CAS #: | 2089047-53-8 |
| Sys. name: | (S)-2-(3-(3-(but-3-yn-1-yl)-3H-diazirin-3-yl)propanamido)-4-methyl-N-(naphthalen-2-yl)pentanamide |
| Mol. wt.: | 404.51 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
CGP201725 was discovered from a screen for compounds that promoted the differentiation of 3T3-L1 mouse preadipocytes to adipocytes by mechanisms distinct from that of the PPARγ agonist rosiglitazone. CGP201725 (10 µM) induced key adipogenic markers (e.g., Pparg, Fabp4, Cd36) in differentiating 3T3-L1s, human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs), 10T1/2 cells, and primary brown preadipocytes. Comparative chemoproteomic studies in 3T3-L1s with inactive compound CGP201726 revealed PGRMC2 as the target of CGP201725, and site-of-labeling studies indicated that it binds in the protein’s cytochrome b5 heme-binding domain. Hemin (IC50 = 40 µM) and protoporphyrin IX (IC50 = 0.13 µM) competed CGP201725 (10 µM) labeling of overexpressed PGRMC2 in HEK293T cells.
|
|
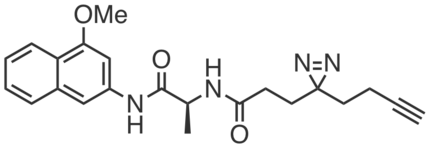
|
|
| Name: | CGP201726 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Photoaffinity probe; control for CGP201725/CGP201727 |
| PubChem CID: | 132274147 |
| CAS #: | 2089058-18-2 |
| Sys. name: | (S)-3-(3-(but-3-yn-1-yl)-3H-diazirin-3-yl)-N-(1-((4-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)amino)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)propanamide |
| Mol. wt.: | 329.46 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
CGP201726 is an inactive compound structurally similar to CGP201725 which did not promote adipogenesis or engage PGRMC2 (at 10 µM). Because it still has photoreactive and clickable groups, it was used as a control probe in chemoproteomic studies to determine that PGRMC2 is the relevant target of CGP201725.
|
|
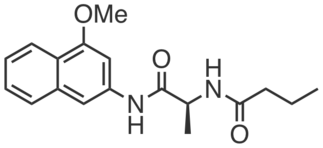
|
|
| Name: | CGP201728 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Control compound for CGP201725/CGP201727 |
| PubChem CID: | 132274148 |
| CAS #: | 2094991-63-4 |
| Sys. name: | (S)-N-(1-((4-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)amino)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)butyramide |
| Mol. wt.: | 314.39 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
CGP201728 is an inactive compound structurally similar to CGP201725 which did not promote adipogenesis or engage PGRMC2 (at 10 µM). It does not bear photoreactive or clickable groups.
|
|
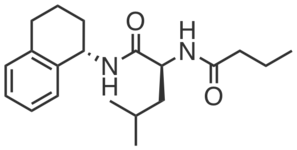
|
|
| Name: | CGP201729 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Control compound for CGP201725/CGP201727 |
| PubChem CID: | 132274149 |
| CAS #: | 2089060-72-8 |
| Sys. name: | (S)-2-butyramido-4-methyl-N-((S)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl)pentanamide |
| Mol. wt.: | 330.47 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
CGP201729 is an inactive compound structurally similar to CGP201725 which did not promote adipogenesis or engage PGRMC2 (at 10 µM). It does not bear photoreactive or clickable groups.
|
|
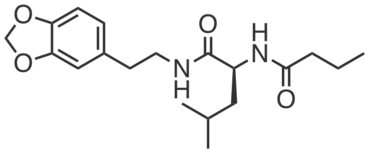
|
|
| Name: | CGP201730 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Control compound for CGP201725/CGP201727 |
| PubChem CID: | 132274150 |
| CAS #: | 2089060-74-0 |
| Sys. name: | (S)-N-(2-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)ethyl)-2-butyramido-4-methylpentanamide |
| Mol. wt.: | 348.44 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
CGP201730 is an inactive compound structurally similar to CGP201725 which did not promote adipogenesis or engage PGRMC2 (at 10 µM). It does not bear photoreactive or clickable groups.
|
|
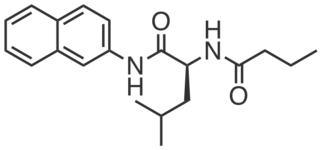
|
|
| Name: | CPAG-1 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Gain-of-function ligand |
| PubChem CID: | 132274146 |
| CAS #: | 2094991-62-3 |
| Sys. name: | (S)-2-butyramido-4-methyl-N-(naphthalen-2-yl)pentanamide |
| Synonyms: | CGP201727 |
| Mol. wt.: | 326.44 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
CPAG-1 is an active analog of CGP201725 which promoted adipogenesis in 3T3-L1s and hMSCs (human mesenchymal stem cells). CPAG-1 lacks the photoreactive and clickable groups present in CGP201725 and dose-dependently competed CGP201725 (10 µM) labeling of overexpressed PGRMC2 in HEK293T cells. Treatment of diet-induced obese (DIO) mice with CPAG-1 (45 mg⋅kg−1) had no effect on weight or food intake, but treated mice had reduced fasting glycemia and insulin levels and improved glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity Brown adipose tissue (BAT) histology showed decreased lipid content and an increase in multilocular adipocytes, features indicative of improved function. Histology of epididymal white adipose tissue (WAT) revealed a marked improvement in CPAG-1-treated mice, with fibrosis and inflammation noticeably decreased.
|
|
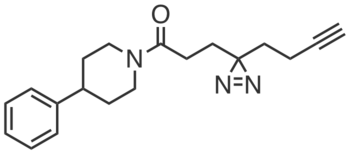
|
|
| Name: | CGP201708 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | 132274143 |
| CAS #: | 2089059-93-6 |
| Sys. name: | 3-(3-(but-3-yn-1-yl)-3H-diazirin-3-yl)-1-(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)propan-1-one |
| Mol. wt.: | 310.40 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
CGP201708 is a photoreactive clickable fragment probe that bears a phenylpiperidine group. CGP201708 (20 or 200 µM) was found to enrich hundreds of proteins, including PTGR2, from HEK293T cells.
|
|
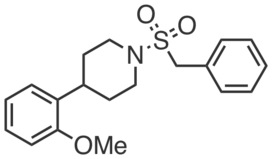
|
|
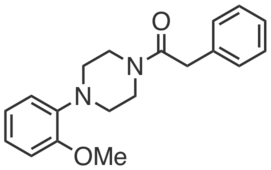
| Name: | KNJ51 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Control compound for |
| PubChem CID: | 132274142 |
| CAS #: | 2094991-61-2 |
| Sys. name: | 1-(benzylsulfonyl)-4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperidine |
| Synonyms: | CGP201723 |
| Mol. wt.: | 345.46 |
| Suppliers: | Request |
|
KNJ51 is a structurally-related control compound for KNJ57 that does not inhibit PTGR2. KNJ51 (100 µM) did not inhibit recombinant PTGR2 and had no effect on 15-keto-PGE2-dependent PPARγ transcriptional activity in PTGR2-transfected HEK293T cells.
|
|
|
|
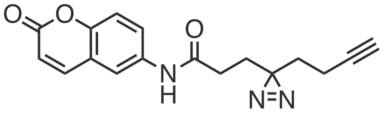
| Name: | KNJ57 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | 16656440 |
| CAS #: | 349093-44-3 |
| Sys. name: | 1-(4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-2-phenylethan-1-one |
| Synonyms: | CGP201722 |
| Mol. wt.: | 310.40 |
| Suppliers: | Aurora Lab Network |
|
KNJ57 is an optimized inhibitor of the prostaglandin-metabolizing enzyme PTGR2. KNJ57 (0.5 µM, ~80%; 5 µM, 100% inhibition) selectively blocked CGP201708 (20 µM) labeling of endogenous PTGR2 in HEK293T cells, without engaging ZADH2, another reductase enzyme that has high sequence similarity to PTGR2. KNJ57 (IC50 = 0.55 µM) inhibited recombinant PTGR2, blocking the production of 13, 14-dihydro-15-keto prostaglandin E2 from 15-keto prostaglandin E2. KNJ57 (0.6 – 5 µM) increased 15-keto-PGE2-dependent PPARγ transcriptional activity in PTGR2-transfected HEK293T cells.
|
|
|
|
| Name: | CGP201703 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Photoaffinity probe |
| PubChem CID: | 132274144 |
| CAS #: | 2089043-46-7 |
| Sys. name: | 3-(3-(but-3-yn-1-yl)-3H-diazirin-3-yl)-N-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)propanamide |
| Mol. wt.: | 309.33 |
| Suppliers: | Aurora LabNetwork Life Chemicals |
|
CGP201703 is a photoreactive clickable fragment probe that bears a chromenone group. CGP201703 (20 or 200 µM) was found to enrich hundreds of proteins, including SLC25A20, from HEK293T cells.
|
|
|
|
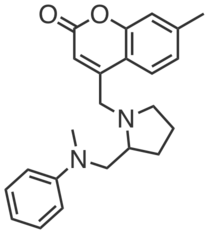
| Name: | CGP201721 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Inhibitor |
| PubChem CID: | 47089244 |
| CAS #: | 1241469-17-9 |
| Sys. name: | 7-methyl-4-((2-((methyl(phenyl)amino)methyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl)-2H-chromen-2-one |
| Mol. wt.: | 362.47 |
| Suppliers: | Aurora Enamine |
|
CGP201721 was identified as a relatively selective competitor of the mitochondrial carnitine/acylcarnitine transporter SLC25A20 in competitive chemoproteomic experiments with photoaffinity probe CGP201703 in HEK293T cells. CGP201721 (20–100 µM) increased long-chain (C16, C18, C18:1) acylcarnitines (~5-20 fold) and decreased exogenous fatty acid oxidation (~60-90% inhibition) in HSC-5 cells.
|
|
|
|
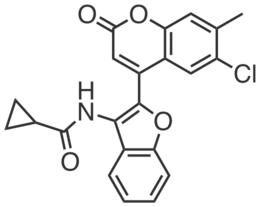
| Name: | CGP201724 |
|---|---|
| Activity: | Control compound for CGP201721 |
| PubChem CID: | 24280187 |
| CAS #: | 929490-21-1 |
| Sys. name: | N-(2-(6-chloro-7-methyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-yl)benzofuran-3-yl)cyclopropanecarboxamide |
| Mol. wt.: | 362.47 |
| Suppliers: | Aurora LabNetwork Life Chemicals |
|
CGP201724 is a structurally-related inactive analog of CGP201721 that does not engage SLC25A20. CGP201724 (100 µM) had no effect on long-chain acylcarnitines or fatty acid oxidation in HSC-5 cells.
|
|